Arduino Programming
Arduino because they think programming is scary. Because of this, we wanted to make sure this tutorial was written for the absolute beginner with no experience whatsoever. This tutorial is a high level view of all the parts and pieces of the Arduino ecosystem. In future posts, we will take you step by step in creating your first simple. Extending the Arduino programming language. Like most other coding languages, the Arduino language allows you to import external libraries. To put it shortly, a library is a set of prewritten code that provides you with extra features. If the built-in libraries are not enough for you, you can download them online or even write your own.
How can you write programs for your Arduino board?
Arduino, natively, supports a language that we call the Arduino Programming Language, or Arduino Language.
This language is based upon the Wiring development platform, which in turn is based upon Processing, which if you are not familiar with, is what p5.js is based upon. It’s a long history of projects building upon other projects, in a very Open Source way. The Arduino IDE is based upon the Processing IDE, and the Wiring IDE which builds on top of it.
When we work with Arduino we commonly use the Arduino IDE (Integrated Development Environment), a software available for all the major desktop platforms (macOS, Linux, Windows), which gives us 2 things: a programming editor with integrated libraries support, and a way to easily compile and load our Arduino programs to a board connected to the computer.
The Arduino Programming Language is basically a framework built on top of C++. You can argue that it’s not a real programming language in the traditional term, but I think this helps avoiding confusion for beginners.
A program written in the Arduino Programming Language is called sketch. A sketch is normally saved with the .ino extension (from Arduino).
The main difference from “normal” C or C++ is that you wrap all your code into 2 main functions. You can have more than 2, of course, but any Arduino program must provide at least those 2.
One is called setup(), the other is called loop(). The first is called once, when the program starts, the second is repeatedly called while your program is running.
We don’t have a main() function like you are used to in C/C++ as the entry point for a program. Once you compile your sketch, the IDE will make sure the end result is a correct C++ program and will basically add the missing glue by preprocessing it.
Everything else is normal C++ code, and as C++ is a superset of C, any valid C is also valid Arduino code.
One difference that might cause you troubles is that while you can spawn your program over multiple files, those files must all be in the same folder. Might be a deal breaking limitation if your program will grow very large, but at that point it will be easy to move to a native C++ setup, which is possible.
Part of the Arduino Programming Language is the built-in libraries that allow you to easily integrate with the functionality provided by the Arduino board.
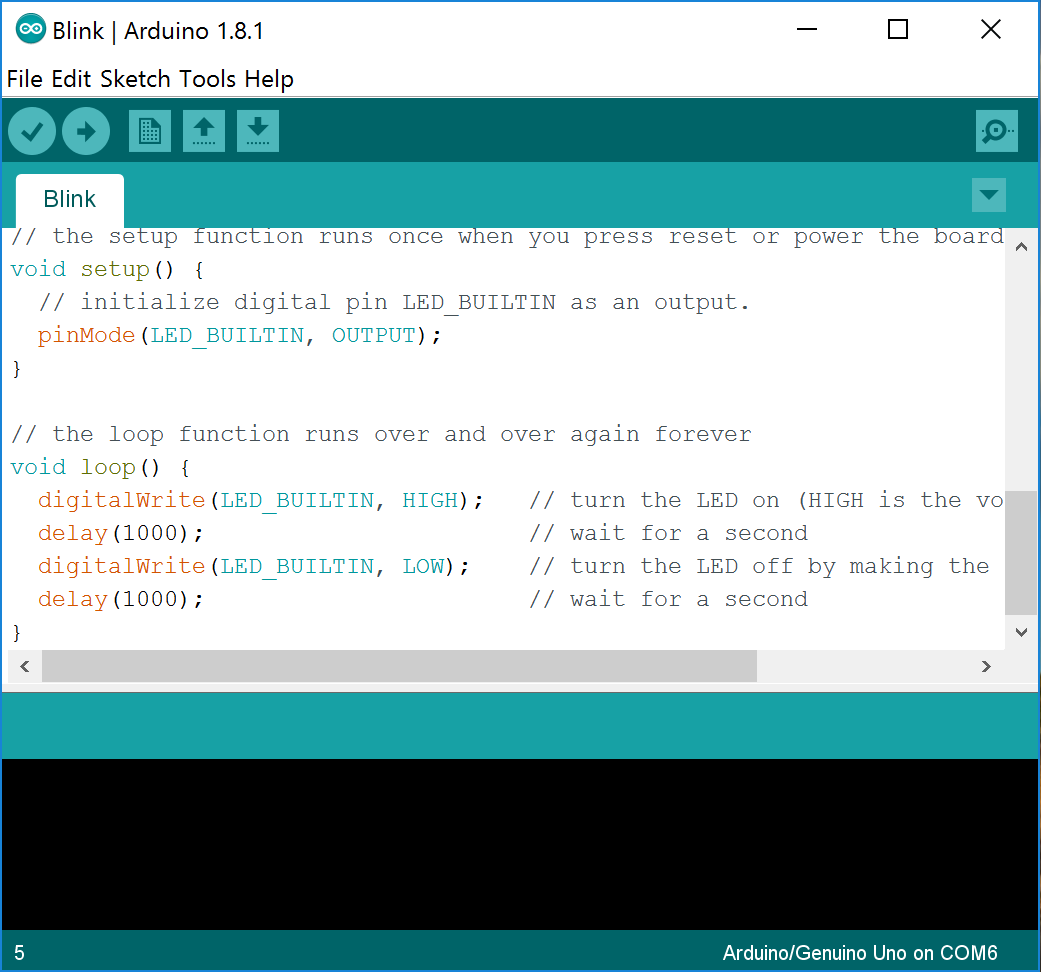
Your first Arduino program will surely involve making a led turn on the light, and then turn off. To do so, you will use the pinMode(), delay() and digitalWrite() functions, along with some constants like HIGH, LOW, OUTPUT.
Like this, the canonical first Arduino project (the “Hello, World!”):
This is all part of the Arduino Programming Language, or we’d better call it suite or library.
Support for other language
As a reminder, I want to note that you are not limited to using this language and IDE to program an Arduino. Projects exist, among others, to let you run Node.js code on it using the Johnny Five project, Python code using pyserial and Go code with Gobot, but the Arduino Programming Language is definitely the one you’ll see most tutorials based upon, since it’s the native and canonical way to work with these devices.
The Arduino Programming Language Built-in constants
Arduino sets two constants we can use to
HIGH equates to a high level of voltage, which can differ depending on the hardware (>2V on 3.3V boards like Arduino Nano, >3V on 5V boards like Arduino Uno)LOW equates to a low level of voltage. Again, the exact value depends on the board used
Then we have 3 constants we can use in combination with the pinMode() function:
INPUTsets the pin as an input pinOUTPUTsets the pin as an output pinINPUT_PULLUPsets the pin as an internal pull-up resistor
The other constant we have is LED_BUILTIN, which points to the number of the on-board pin, which usually equates to the number 13.
In addition to this, we have the C/C++ constants true and false.
Arduino Math Constants
M_PIthe constant pi (3.14159265358979323846)M_Ethe constant eM_LN10the natural logarithm of the number 10.M_LN2the natural logarithm of the number 2.M_LOG10Ethe logarithm of the e to base 10.M_LOG2Ethe logarithm of the e to base 2.M_SQRT2the square root of 2.NANthe NAN (not a number) constant.
The Arduino Programming Language Built-in Functions
In this section I am going to make a reference for the built-in functions provided by the Arduino Programming Language.
Program lifecycle

setup()this function is called once, when the program starts, and when the Arduino is shut down and restarted.loop()this function is repeatedly called while the Arduino program is running.
Arduino Programming List
Handling I/O
The following functions help with handling input and output from your Arduino device.
Digital I/O
digitalRead()reads the value from a digital pin. Accepts a pin number as a parameter, and returns theHIGHorLOWconstant.digitalWrite()writes aHIGHorLOWvalue to a digital output pin. You pass the pin number andHIGHorLOWas parameters.pinMode()sets a pin to be an input, or an output. You pass the pin number and theINPUTorOUTPUTvalue as parameters.pulseIn()reads a digital pulse fromLOWtoHIGHand then toLOWagain, or fromHIGHtoLOWand toHIGHagain on a pin. The program will block until the pulse is detected. You specify the pin number and the kind of pulse you want to detect (LHL or HLH). You can specify an optional timeout to stop waiting for that pulse.pulseInLong()is same aspulseIn(), except it is implemented differently and it can’t be used if interrupts are turned off. Interrupts are commonly turned off to get a more accurate result.shiftIn()reads a byte of data one bit at a time from a pin.shiftOut()writes a byte of data one bit at a time to a pin.tone()sends a square wave on a pin, used for buzzers/speakers to play tones. You can specify the pin, and the frequency. It works on both digital and analog pins.noTone()stops thetone()generated wave on a pin.
Analog I/O
analogRead()reads the value from an analog pin.analogReference()configures the value used for the top input range in the analog input, by default 5V in 5V boards and 3.3V in 3.3V boards.analogWrite()writes an analog value to a pinanalogReadResolution()lets you change the default analog bits resolution foranalogRead(), by default 10 bits. Only works on specific devices (Arduino Due, Zero and MKR)analogWriteResolution()lets you change the default analog bits resolution foranalogWrite(), by default 10 bits. Only works on specific devices (Arduino Due, Zero and MKR)

Time functions
delay()pauses the program for a number of milliseconds specified as parameterdelayMicroseconds()pauses the program for a number of microseconds specified as parametermicros()the number of microseconds since the start of the program. Resets after ~70 minutes due to overflowmillis()the number of milliseconds since the start of the program. Resets after ~50 days due to overflow
Math functions
Arduino Programming Language
abs()the absolute value of a numberconstrain()constrains a number to be within a range, see usagemap()re-maps a number from one range to another, see usagemax()the maximum of two numbersmin()the minimum of two numberspow()the value of a number raised to a powersq()the square of a numbersqrt()the square root of a numbercos()the cosine of an anglesin()the sine of an angletan()the tangent of an angle
Note: there are more built-in mathematical functions if you need them, documented here.
Working with alphanumeric characters
isAlpha()checks if a char is alpha (a letter)isAlphaNumeric()checks if a char is alphanumeric (a letter or number)isAscii()checks if a char is an ASCII characterisControl()checks if a char is a control characterisDigit()checks if a char is a numberisGraph()checks if a char is a printable ASCII character, and contains content (it is not a space, for example)isHexadecimalDigit()checks if a char is an hexadecimal digit (A-F 0-9)isLowerCase()checks if a char is a letter in lower caseisPrintable()checks if a char is a printable ASCII characterisPunct()checks if a char is a punctuation (a comma, a semicolon, an exclamation mark etc)isSpace()checks if a char is a space, form feedf, newlinen, carriage returnr, horizontal tabt, or vertical tabv.isUpperCase()checks if a char is a letter in upper caseisWhitespace()checks if a char is a space character or an horizontal tabt
Random numbers generation
random()generate a pseudo-random numberrandomSeed()initialize the pseudo-random number generator with an arbitrary initial number
In Arduino, like in most languages, it’s impossible to get really random numbers, and the sequence is always the same, so you seed it with the current time or (in the case of Arduino) you can read the input from an analog port.
Working with bits and bytes
bit()computes the value of a bit (0 = 1, 1 = 2, 2 = 4, 3 = 8…)bitClear()clear (sets to 0) a bit of a numeric variable. Accepts a number, and the number of the bit starting from the rightbitRead()read a bit of a number. Accepts a number, and the number of the bit starting from the rightbitSet()sets to 1 a bit of a number. Accepts a number, and the number of the bit starting from the rightbitWrite()write 1 or 0 to a specific bit of a number Accepts a number, the number of the bit starting from the right, and the value to write (0 or 1)highByte()get the high-order (leftmost) byte of a word variable (which has 2 bytes)lowByte()get the low-order (rightmost) byte of a word variable (which has 2 bytes)
Interrupts
noInterrupts()disables interruptsinterrupts()re-enables interrupts after they’ve been disabledattachInterrupt()allow a digital input pin to be an interrupt. Different boards have different allowed pins, check the official docs.detachInterrupt()disables an interrupt enabled usingattachInterrupt()
